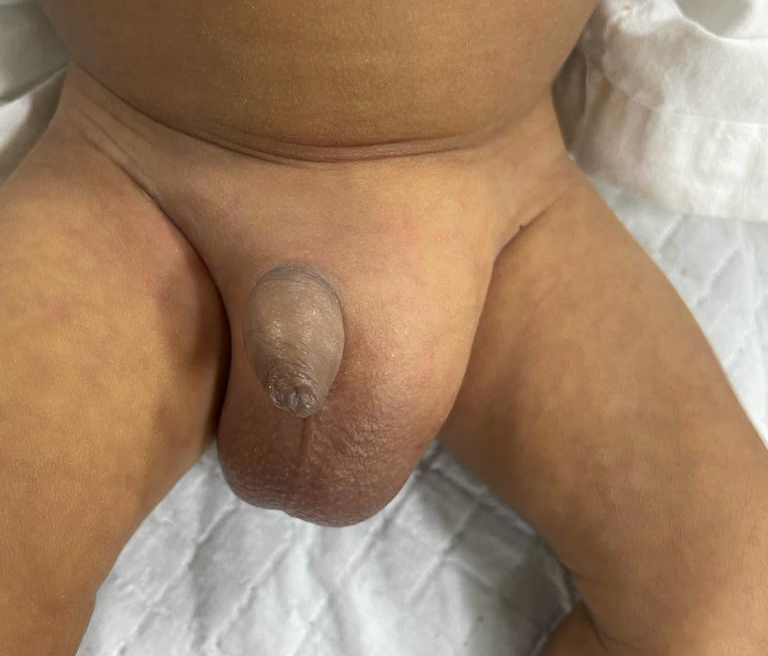
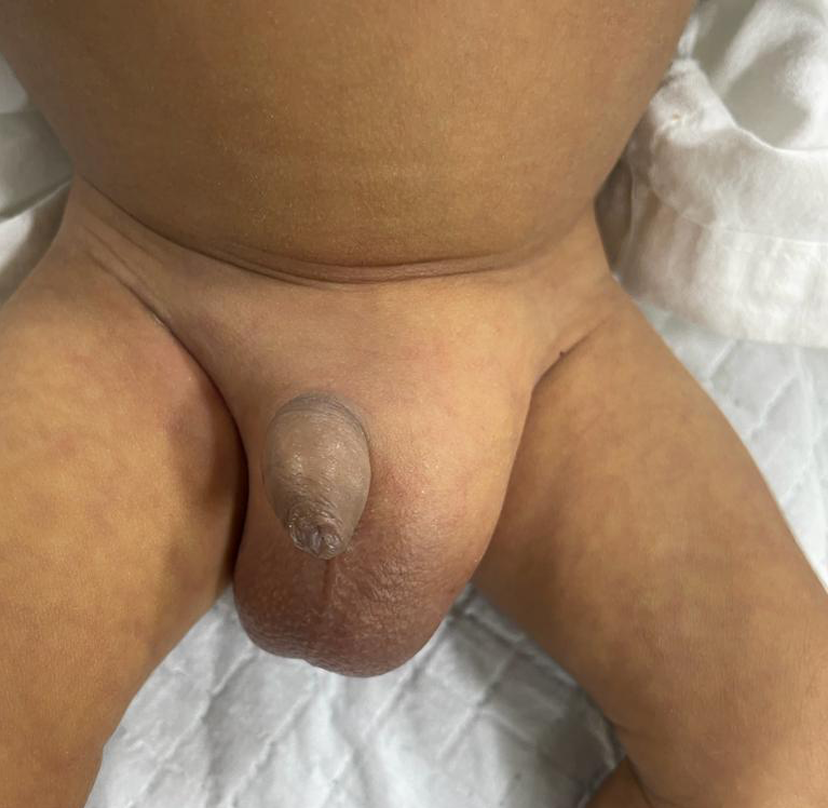
Hernias
When an organ pulls through a tear in the muscle or tissue holding it in place, a hernia results. For instance, a weak spot in the abdominal wall may be breached by the intestines.
Hernias are common in the area of your abdomen between your chest and hips, but they can also develop in the region of your upper thighs and groyne.
While most hernias don't pose a life-threatening hazard right away, they also don't go away on their own. Surgery may occasionally be necessary to avoid potentially serious side effects.